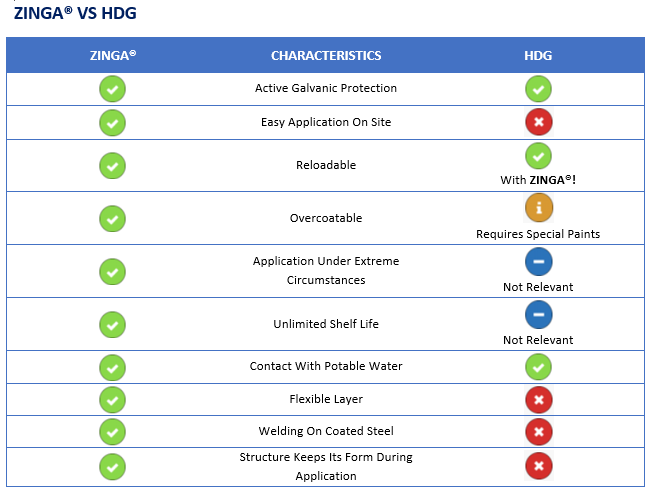
ZINGA VS Hot Dip Galvanizing (HDG)
|
ZINGA® |
HDG |
|
Active
Cathodic Protection |
|
ZINGA® has the most important advantage that it
offers a real cathodic (galvanic) protection. ZINGA® has a concentration of
96% special zinc in its dry layer which gives it its galvanic
characteristics. The film galvanizing system ZINGA® (also called
“Zinganization®“) shows comparable protection to HDG and in some
circumstances even superior protection (e.g. in immersion). |
|
Steel members which have been hot dip
galvanized have proven cathodic protection by the sacrification of the Zinc
on the surface. Damages to the steel substrate show protection by the
throwing power of the zinc layer. The Zinc layer diminishes because of the
depletion of the Zinc. |
|
For more information please see “How
Does It Work?” |
|
Easy
Application On Site |
|
ZINGA® can be applied in the same way as
paints. |
|
Hot dip galvanization cannot be applied on
site, the structure has to be dismantled; transported to the hot dip planted;
hot dipped, transported back to site and reassembled. |
|
For more information please see “Application?” |
|
Reloadable |
|
A cured ZINGA® layer, will reliquidize if a new
layer of ZINGA® is applied. This ensures the creation of 1 ZINGA® layer with
a continuous electrochemical contact between the Zinc particles and thus
galvanic protection. If the ZINGA® layer is very old, the Zinc salts on the
surface (ensuring a passive protection), need to be removed to ensure
complete reliquidization; this can be obtained by performing a light sweep
blast. |
|
Hot dipped structures cannot be hot dipped
again unless they are dismantled, blasted and dipped into the Zinc bath. ZINGA®‘s
mechanism of protection is so similar to conventional galvanizing that they
work in complete unison, as they are merely different forms of zinc. Rather
than replacing galvanized assets, structures can simply have their protection
“recharged” by applying ZINGA® to the rough surface of the old galvanizing
after appropriate decontamination and removal of the salts. |
|
For more information please see “Characteristics
/ Advantages” and “Application?” |
|
Overcoatable |
|
ZINGA® can be overcoated with a fast drying,
compatible paint. Care should be taken to avoid affection of the Zinc layer
by aggressive solvents of the topcoat. |
|
Not only does HDG requires specialized,
compatible paints; a thorough surface preparation is also needed before the
application of a topcoat on HDG. This includes alkaline or acid rinsing and
sweep blasting the surface. |
|
For more information please see “Overcoating
of ZINGA®” |
|
Application
Under Extreme Circumstances |
|
ZINGA® can be applied in a wide variety of
weather conditions. The application surface temperature range is from -15°C
to +40°C with a maximum humidity of 95% so long as the dew point is 3°C above
the steel temperature. |
|
Not applicable. A HDG layer is applied in the
hot dip plant.
|
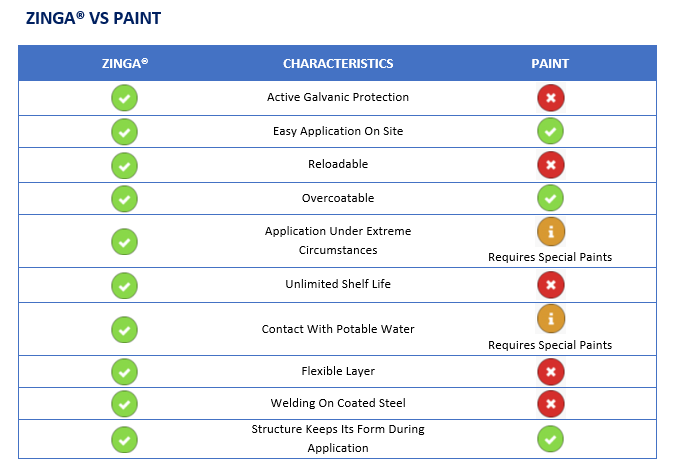
|
ZINGA® |
HDG |
|
Unlimited
Shelf Life |
|
|
ZINGA® has unlimited shelf life. This means it
is possible to always have ZINGA® in storage for touch up or for future
projects. |
|
Not applicable. |
|
Contact
With Potable Water |
|
ZINGA® only contains non-toxic elements in its
dry layer (after evaporation of the solvent). Therefore it can be, and has
been, used in contact with potable water. Since the ZINGA® remains active, it
produces Zinc salts which dissolve in the water. This can sometimes lead to
small precipitations in the water, which are however nontoxic. To avoid this,
we recommend to wash the surface very thoroughly with fresh water. For more
information, contact a Zingametall representative. |
|
The American Water Works Association (AWWA)
allows the use of galvanized steel for water storage tanks. Only galvanizers
that have submitted test coupons of their galvanized steel and have been
approved by the NSF have the authority to galvanize steel for use with
potable water. |
|
Flexible
Layer |
|
ZINGA®, containing 96% Zinc in the dry layer
has very few binder. In fact, not every Zinc particle is completely
surrounded by resin. This also explains why the ZINGA® layer is rough and
porous. However, this is why ZINGA® behaves like a metal when it comes to
impact and bending. ZINGA® can be bent over very small angles without showing
cracks in the dry layer. |
|
When hot-dipped structures are bent over a
certain angle, the coating will be affected and the total structure will need
to be hot-dipped again to restore the coating. It is also recommended to
restore these coatings by using a zinc rich liquid coating (like ZINGA®).
In general, it is advised to bend the
structures before hot-dipping. In practice, this is not always possible (e.g.
pipes that need to be fitted to form connections). |
|
Welding
On Coated Steel |
|
Zinganized® steel can be welded without the
release of any toxic fumes (tested according BS 6853) and with a very small
burn back. Since the ZINGA® is not in any way alloyed with the steel, there
is no danger of zinc inclusion in the weld. |
|
Welds are advised on steel free of zinc to
prevent strength reduction through zinc inclusion in the weld itself (since
the Zinc is molten into the steel - alloy). The zinc coating should be
removed at least one to four inches from either side of the intended weld
zone and on both sides of the steel part. Grinding is the most effective
means of removing the galvanized coating. |
|
Structure
Keeps Its Form During Application |
|
ZINGA® is applied under ambient temperature and
does not deform the structure. |
|
With hot-dip galvanization, deformation of the
structure is possible due to the use of high temperatures of molten Zinc.
There is also potential for hydrogen embrittlement within welds. This can
lead to problems when structures are precisely measured in a steel structure
to form connections. |

-2721-p.png)





1 Comment
Apurbo Ray
Testing Message